Documentation
System Overview
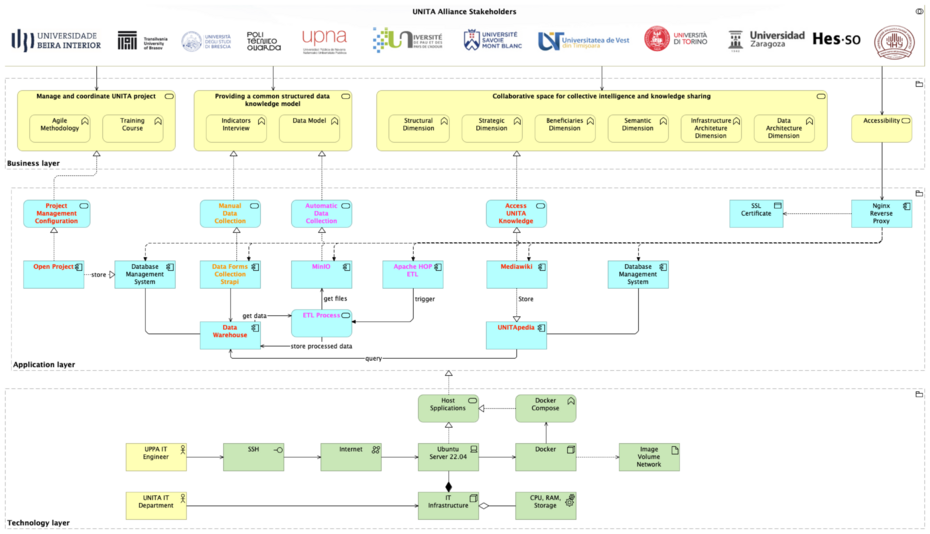
The UNITApedia system is composed of two integrated main components designed to enhance data accessibility, transparency, and collaboration among UNITA members. It connects a shared data warehouse with a MediaWiki-based front-end, creating a dynamic and scalable ecosystem for data visualization, management, and analysis.
Acts as the central repository for structured data such as deliverables, indicators, and progress metrics. Utilizes metadata, ontology, and semantic web technologies to provide a comprehensive, interconnected view of data collected across all UNITA members. Supports efficient data centralization, organization, and analysis, ensuring a unified understanding of the data ecosystem. Backed by PostgreSQL, enabling complex queries, scalability, and robust data storage. Alongside Apache HOP as an ETL to develop powerful data pipelines.
MediaWiki-Based Front-End Interface
Provides a user-friendly system for monitoring project progress, visualizing metrics, and assessing impact. Acts as the primary user interface, powered by extensions like External Data, Scribunto, and Semantic MediaWiki. Dynamically retrieves data through its API layer, integrating seamlessly with the data warehouse. Enhances decision-making and collaboration by providing stakeholders with real-time, actionable insights. Share and collaborate with other users to extend the UNITA knowledge-base.
Key Features
- Near real-time integrated data pipeline processus:
- Utilizes robust APIs to fetch and display updated information from the PostgreSQL database.
- Near-instantaneous process from data extraction to final result display on UNITApedia.
- User-Friendly Interface:
- Built on MediaWiki, ensuring an intuitive experience for users of varying technical backgrounds.
- Extensions like Page Forms and Semantic MediaWiki simplify data input, annotation, and querying.
- Open Source:
- Designed with modularity and scalability in mind, allowing deployment across other UNITA members or similar institutions.
- Supports customization to meet unique institutional needs while adhering to UNITA’s vision.
- Dynamic Queries:
- Uses optimized prepared PostgreSQL statements and Lua scripting via MediaWiki extensions to deliver efficient and dynamic data visualization.
- Allows advanced customization of data presentation formats based on user needs.
- Scalable Architecture:
- Employs a Dockerized infrastructure for each subsystem (MediaWiki, Strapi, PostgreSQL, Apache HOP, etc.), ensuring modularity and scalability.
- Supports efficient deployment, updates, and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Transparency:
- Enables cross-institutional collaboration by centralizing data in the shared warehouse.
- Provides stakeholders with real-time visualizations, ensuring informed decision-making and alignment with organizational goals.
System Architecture
The following considerations shaped the UNITApedia architecture:
- Modularity & Scalability
- Docker ensures each service is isolated, easily updated, and can be scaled independently if usage grows.
- Clear separation of roles (Strapi for input, Apache HOP for ETL, MediaWiki for output) streamlines development and maintenance.
- Open-Source & Extensibility
- MediaWiki: Chosen for its mature ecosystem (extensions like Semantic MediaWiki, External Data, Page Forms) and robust community support.
- PostgreSQL: Offers advanced query capabilities, reliability, and easy integration with Apache HOP.
- MinIO: An open-source, S3-compatible object store that fits seamlessly into containerized deployments.
- Security & SSL
- Nginx-Proxy + ACME Companion: Provides automated certificate management and secure HTTPS connections, protecting data in transit.
- Role-Based Access: Strapi enforces form-level permissions, while MediaWiki can be configured with namespace-based access for sensitive data.
- Data Consistency & Quality
- Apache HOP ETL: Ensures data from different sources (Strapi, MinIO CSVs) is validated, cleaned, and structured before landing in the datamart.
- Semantic MediaWiki: Allows for structured data definitions and cross-referencing, ensuring consistent reporting across tasks and indicators.
- Maintainability & Future Growth
- Each service can be updated or replaced with minimal impact on the others, thanks to Docker’s container-based isolation.
- The architecture can accommodate new data sources, additional tasks/indicators, or new alliances with minimal refactoring.